

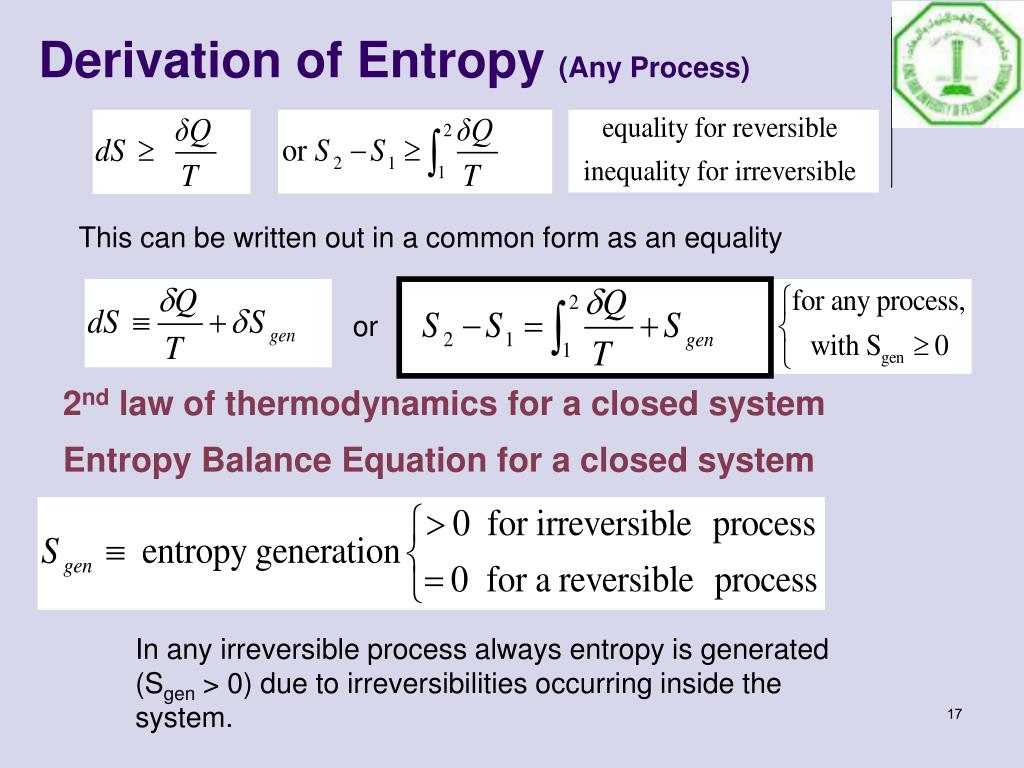
If we consider a hot object in a cold room as our complete system, then the thermal energy in our system is not very well dispersed because it’s more concentrated in the hot object. For example, we know that higher temperature means a greater average thermal energy per molecule, so we can think of temperature as a measure of the concentration of thermal energy in an object. By isolated system we mean one for which energy does not leave or enter. In order to aid in our study of other thermodynamic processes, such as phase changes, a more general version of the Second Law can be stated in terms of energy concentration and dispersion: a ny spontaneous process must move an isolated system toward a state of more uniform dispersion of energy throughout the system. The Second Law of Thermodynamics introduced in the previous chapters states that thermal energy will always spontaneously transfer from higher temperature to lower temperature.
Britannica Beyond We’ve created a new place where questions are at the center of learning.100 Women Britannica celebrates the centennial of the Nineteenth Amendment, highlighting suffragists and history-making politicians.COVID-19 Portal While this global health crisis continues to evolve, it can be useful to look to past pandemics to better understand how to respond today.Student Portal Britannica is the ultimate student resource for key school subjects like history, government, literature, and more.Britannica Explains In these videos, Britannica explains a variety of topics and answers frequently asked questions.Demystified Videos In Demystified, Britannica has all the answers to your burning questions.
This Time in History In these videos, find out what happened this month (or any month!) in history.

#WTFact Videos In #WTFact Britannica shares some of the most bizarre facts we can find.Britannica Classics Check out these retro videos from Encyclopedia Britannica’s archives.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
